Deploying a Hadoop Cluster on Linux VMs in Azure from an ARM Template
This article covers how to deploy a Hadoop Cluster using Apache Ambari running on Linux Virtual Machines in Azure from an ARM Template.
Overview
There are existing options available in the Azure Marketplace for deploying Hadoop in Azure. The first option for Production purposes is HDInsight. By running the a deployment from the Azure Marketplace you can have a cluster setup and ready in less than 30 minutes. Additionally, there is another option avilable from Hortonworks for learning purposes in the Azure Marketplace, Hortonworks Sandbox with HDP 2.4.This will install almost all of the currently available Hadoop services onto a single stand-alone VM.
In my case, I wanted the ability to deploy Hadoop in Azure on Linux VMs of any size of my choosing and to be able to control the entire deployment of Hadoop and Hadoop related services using Apache Ambari. The reason I wanted to go to this level of effort was so that I could learn Hadoop from the standpoint of both an Administrator and a Developer while being able to manage a Hadoop Cluster as a single or multi-node deployment.
Prerequisites
Before deploying the ARM Template below, make sure you have enough VM cores available in your Azure Subscription.
Deploy the new Hadoop Infrastructure to Azure using an ARM Template
Note: This ARM Template should be used for learning and testing purposes, ONLY!
Clicking on the Deploy to Azure button below will deploy the following
- Single Ambari Server VM
- Multiple Hadoop Server VMs
Once the Infrastructure is deployed, the following actions will take place on the Ambari Server VM
- The Ambari Server repo is downloaded and installed on the Ambari VM.
- All deployed Servers will have their /etc/hosts file modified to contain the IP Address, FQDN, and Hostname of all deployed Servers.
- The FQDN for each Server will be based upon the location where the ARM Template is deployed to, i.e. - West Europe = westeurope.cloudapp.azure.com.
- iptables and Transparent Huge Pages is disabled on all Servers.
Some of the options available to you if you decide to test out Hadoop using this ARM Template include:
- Deploying Hadoop to VMs smaller than A3 or DS3v2.
- Deploy Hadoop into a multi-node environment.
- Deploying minimal Hadoop features.
- Deploying only the Hadoop features you want.
While the ability to deploy a Hadoop Cluster to a set of A1 or DS1v2 VMs isn’t recommended, it is still possible. Having the opportunity to figure out several different ways to deploy Hadoop by accidentally breaking it was one of my primary reasons for writing this ARM Template. From my personal experience, breaking a product is a great way to learn it (as long as it isn’t in Production).
Accessing the deployed VMs
All of the deployed VMs are externally accesssible via SSH on Port 22 from their respective Public IP Addresses.
List of all Open Ports for all Hadoop Services can be found in the Network Security Group deployed in the Resource Group.
Retrieve the SSH Private Key and Hadoop FQDNs
In order to deploy a Hadoop Cluster from Ambari without having to manually install agents on all the Servers you want in the Hadoop Cluster, an SSH Private Key must be generated and added to all the Servers. This was previously done as part of the Custom Script that was deployed on the Ambari Server at the very end of the ARM Template Deployment. Now all that is required is to retreive the SSH Private Key.
For this section, the Name of the Ambari Server will be rei-ambarisrv-iy.westeurope.cloudapp.azure.com and the Linux User will be linuxadmin.
Login to the Ambari Server via SSH using the DNS Name of it’s associated Public IP Address. Syntax is below:
<AMBARI_SERVER_NAME>.<LOCATION>.cloudapp.azure.com
Once you are logged in, change over to root. Type the password of the linuxadmin user when prompted.
sudo su
Run the following command to retrieve the FQDNs of all of the Hadoop Servers. This is optional As this information can also be found on the Public IP Address resources associated with the Hadoop Servers.
cat /etc/hosts
Sample Output:
10.0.1.4 rei-ambarisrv-iy.westeurope.cloudapp.azure.com rei-ambarisrv-iy
10.0.1.5 rei-hadoopsrv-iy0.westeurope.cloudapp.azure.com rei-hadoopsrv-iy0
10.0.1.6 rei-hadoopsrv-iy1.westeurope.cloudapp.azure.com rei-hadoopsrv-iy1
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
Next, run the following command to retrieve the SSH Private Key generated during the installation of Ambari.
cat /root/.ssh/id_rsa
Sample Output:
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
MIIEowIBAAKCAQEA3T/N3ShLdpHdosAQ02nsgf3a9aIsv5BRJJMolIkWuiG7xrox
T8L1T+m1/2BsizVdGdjR6gjNSl2HEGsHeBd49kza5SipmnI1W3PYE4YCGzP3/Hor
qjscMfZ5fMVcv9SKnwF2MVDoPcoj+Z/YBeXDcyUP1ygb/o56VnkWyo44KqQCqJ11
zGelmPAm2TrqNxGJk8pWqNqwBSNe2dfxgGpOAUM9cUlQ+JpCkACasQ6RJQcxSRVc
2swrqf3bNb+aWwYNc7r37oOG0L8i3XEzK6LCEOz6NgKORxlpjQ47rC0NkWMevG+H
jC9awZHtI9/wdNI4i91vt2GVRh260sm2cU5nUQIBIwKCAQEA1u2GJ0u3BXfBXEWM
sB3BLdIH500VhuP3DZZErYx8ekynyF0Z9bYS3+pZBrVwwb7PeDG1+UphBml75BAz
JDQPGyYWeDYhGbDGHlNG7mTsGmz/h4yfcirK7rTrC33lEh7tD33DRdmRJhTSfXa0
mAPFLga+7kQ4c6BZldS3Dek94EW+2n+eyBmEySQ2YedDkX1rcr7Fu+aH4ih4q++e
r7IPnRjw4lTjLkD4+JdD0ozg2TMhWMrw2s3apmCzEQkU9wQJ3/s21n1opPHn2TQO
CvxELLzkI4KZEiJGiLDI2xqg4sk24CdbxSTfYVghYRE6Q8z9RW3/wcOWw0e2vDss
MQ00gwKBgQD2+qTnSvwmbRNrlhdfuxiW4C7jXWC3b/nIqIVJO9QXdJ5ZDnczp6jd
Q6Uga5gcpc/MgKVFnp+P5N98RemS8Pi2l5GdHH4OcTtzRxk75we0gxwgaGkmNzNK
98qe7VBipnjQiiVUWy+AfeZk8kfA3YexDBj3lkQcu4xHdl0Bd7i+kwKBgQDlVJNM
76uUmQpHC4hMdUMiNfUvRkjlLFpHJfobgKo1iQs3thFRkkUZtd3hoWz2cnOzZYEQ
PNEroWB5bVu9IHofhKbAfMCbtbfXggvKscSLI4bf5UesXx0wU9jsGYyM1EhZeLhF
qdJdudDPPp0KM2DsMMQtFeMwKvTN1uR/9ERNCwKBgQDhzzeu5XjSrN6OQBVe1vHp
B3tTiJLw22gH6oh9eIdl5vcs2gaVoJpj5hNQ12aAl5lqhD9VmFde/SQZ2YUYoc1z
vcb2C2vv8n9/VvJ/6SudubNQ1H1kxMEumWjL0aiUtXXF+qXJd/Dqgby0ELahtJlR
aiV0pqSsjjccw/1DK6GYSwKBgQCWs+vE2AMJ4Ol/JNXpGduoxF9K86w+1ADPqz30
0OThWg6vlObPNDwJlMUB/F2MAhGEhIgDWypef/2Rn6Kve733dG2Ubzy+GFQ9KZK4
ZjCzNJp139ADjvXsjt8BjSHY40V8n8mM3U+57yLRVQgcpWuT5Yg64n9aKttisclb
ZgD/bQKBgAUKeiA2JYmTn2t22h18wV67XOSPN01/xS1IFGRsKQ6n8K1OisqMIayc
KUmPqnroe2ThQssgae9DDzXY2RnnIOzAfkyUX70KpaFv0bv2xLXjn6pMbjE2N7qc
sym5R8bYdwc4ighupztwMw8HT3uf5DMO7A6uGihaoq1Z+VWYPYKA
-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
Make note of the SSH Private Key for the next section.
Deploying the Hadoop Cluster using Ambari
Apache Ambari enables system administrators to provision, manage and monitor a Hadoop cluster as well as to integrate with an existing enterprise infrastructure. By using Ambari, you can control the deployment, management, and removal of the following Hadoop related services in a Hadoop Cluster.
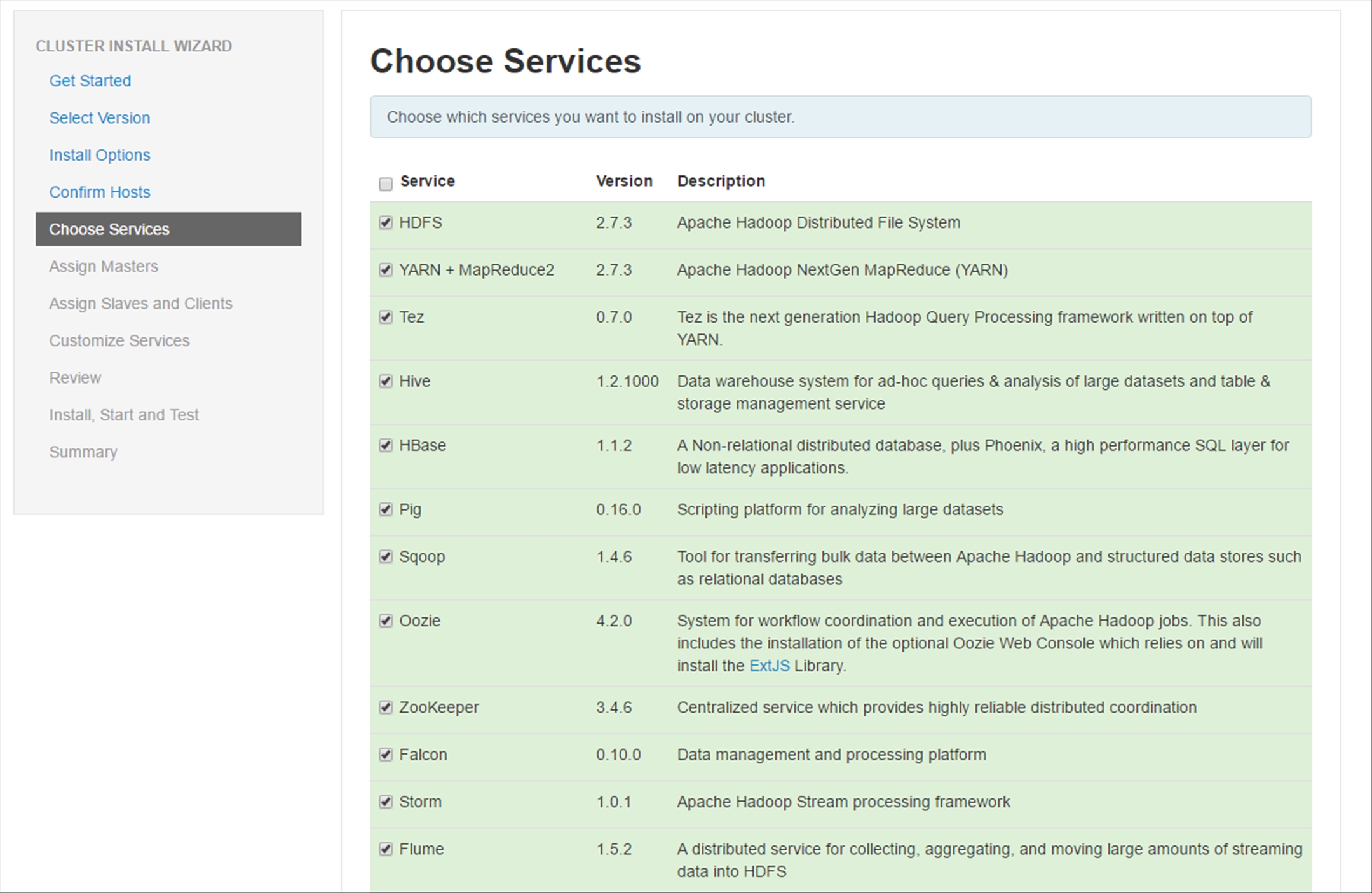
- HDFS
- YARN + MapReduce2
- Tez
- Hive
- HBase
- Pig
- Sqoop
- Oozie
- ZooKeeper
- Falcon
- Storm
- Flume
- Accumulo
- Ambari Infra
- Ambari Metrics
- Atlas
- Kafka
- Knox
- Log Search
- SmartSense
- Spark
- Spark2
- Zeppelin Notebook
- Mahout
- Slider
For this section, the Ambari Web UI will be http://rei-ambarisrv-iy.westeurope.cloudapp.azure.com:8080.
Once the ARM Template Deployment is complete, use the following syntax to access the Ambari Web UI.
http://<AMBARI_SERVER_NAME>.<LOCATION>.cloudapp.azure.com:8080
Next, login to the Ambari Server using the following credentials:
username: admin
password: admin
Next, click on the Launch Install Wizard button under the Create a Cluster section.
Next, type in a name for the Hadoop Cluster and click Next.
Next, make sure HDP-2.5.3.0 is already selected, scroll down to the bottom of the page and click Next.
Next, copy in the FQDN values of the Hadoop Servers that you deployed and the SSH Private Key that you retrieved earlier from the Ambari Server. Afterwards, click on the Register and Confirm button.
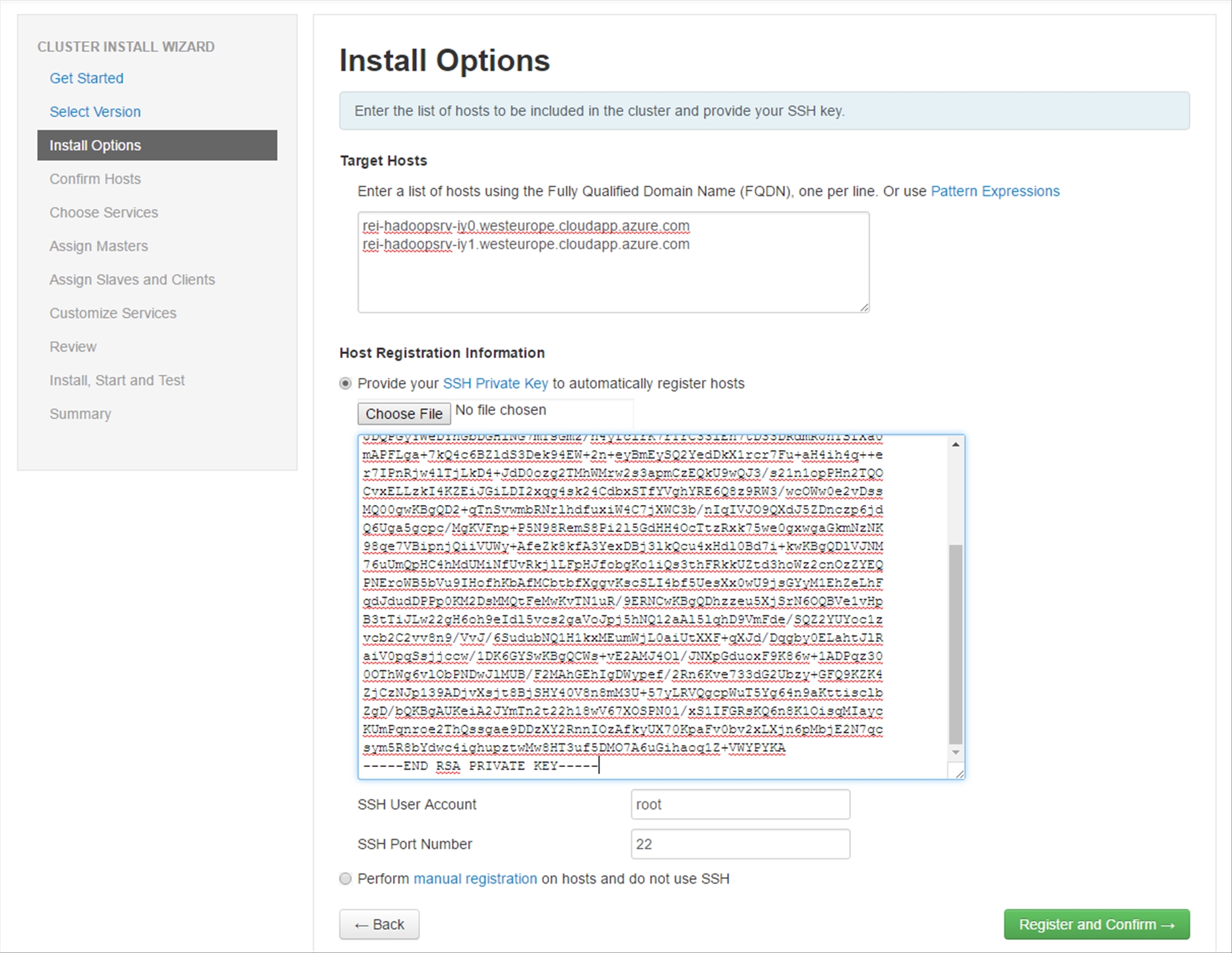
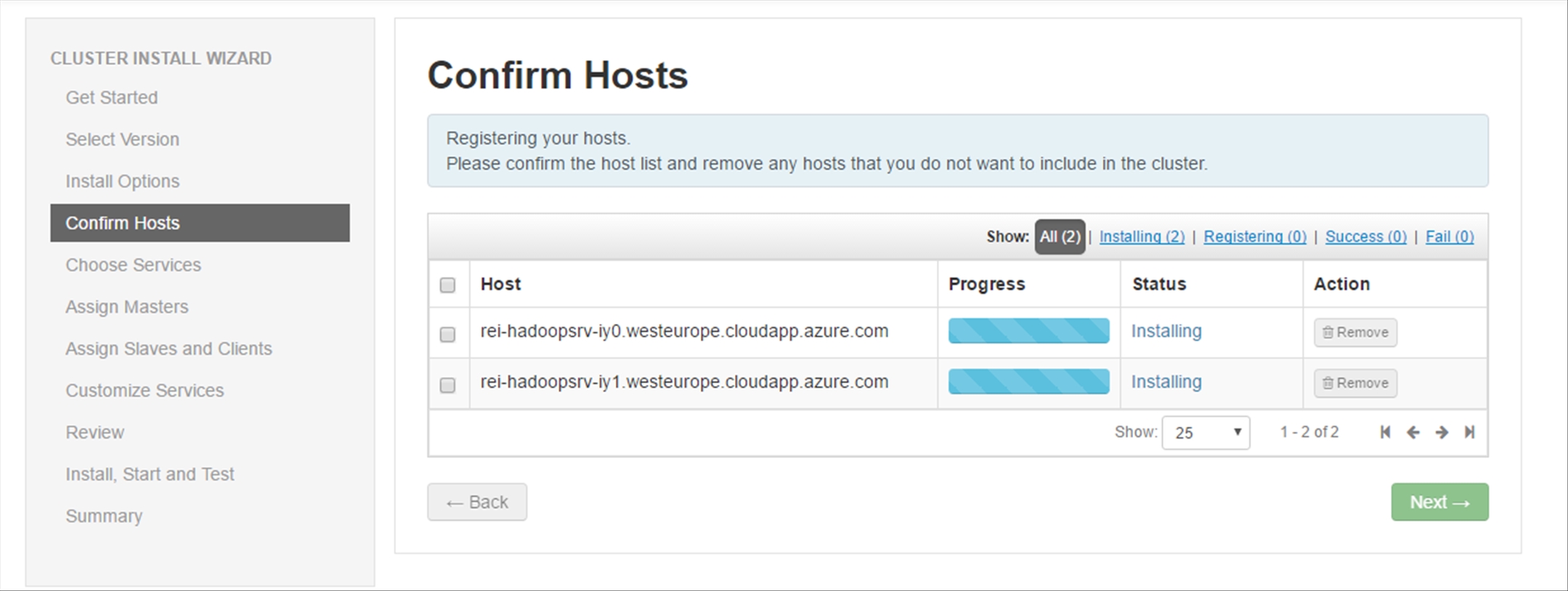
The Hadoop Hosts will be registered and checked for any potential issues, the entire process should only take a couple minutes.
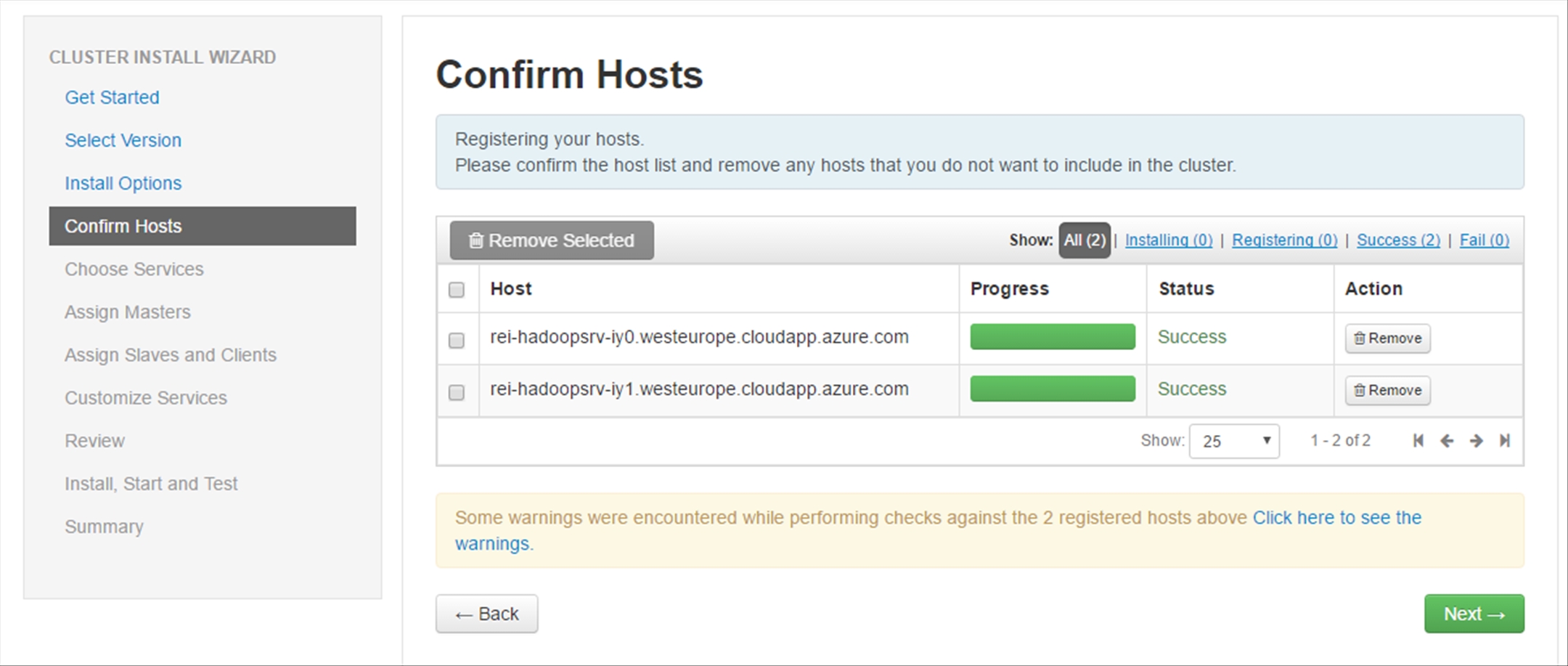
After the registration is completed, ignore the warnings and click on Next.
In the Choose Services section, you have the option to add or remove any of the services you want to install on the Cluster; better still, if you choose a combination that is missing a dependency, you will be prompted what you are missing and to add it. For the purpose of this walkthrough, scroll down to the bottom of the page and click Next.
In the Assign Masters section, you have the option to assign the master components to whichever server you want them to reside on. Leave the configuration as is by default, scroll down to the bottom of the page and click Next.
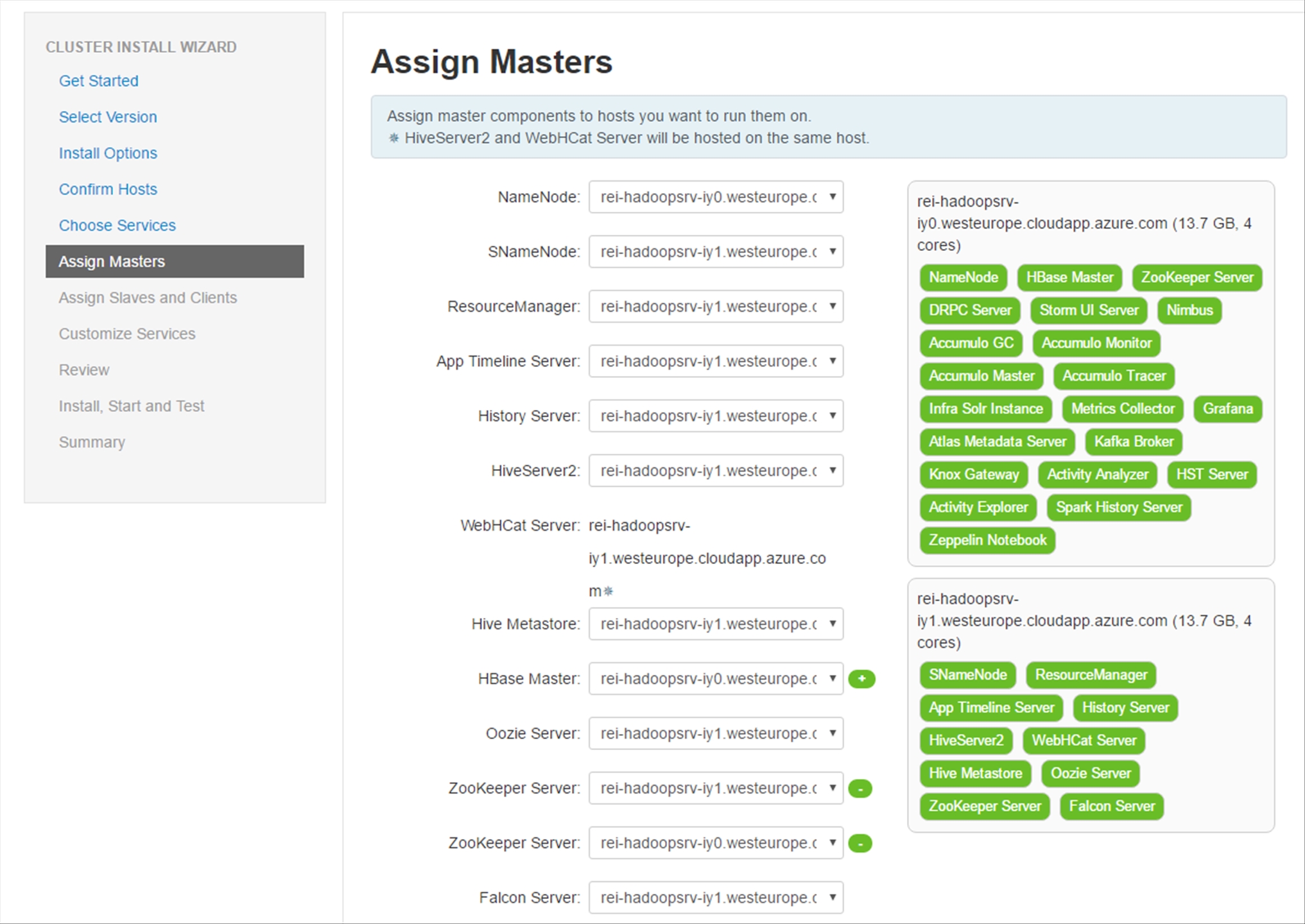
In the Assign Slaves and Clients section, leave the default values as is and click Next.
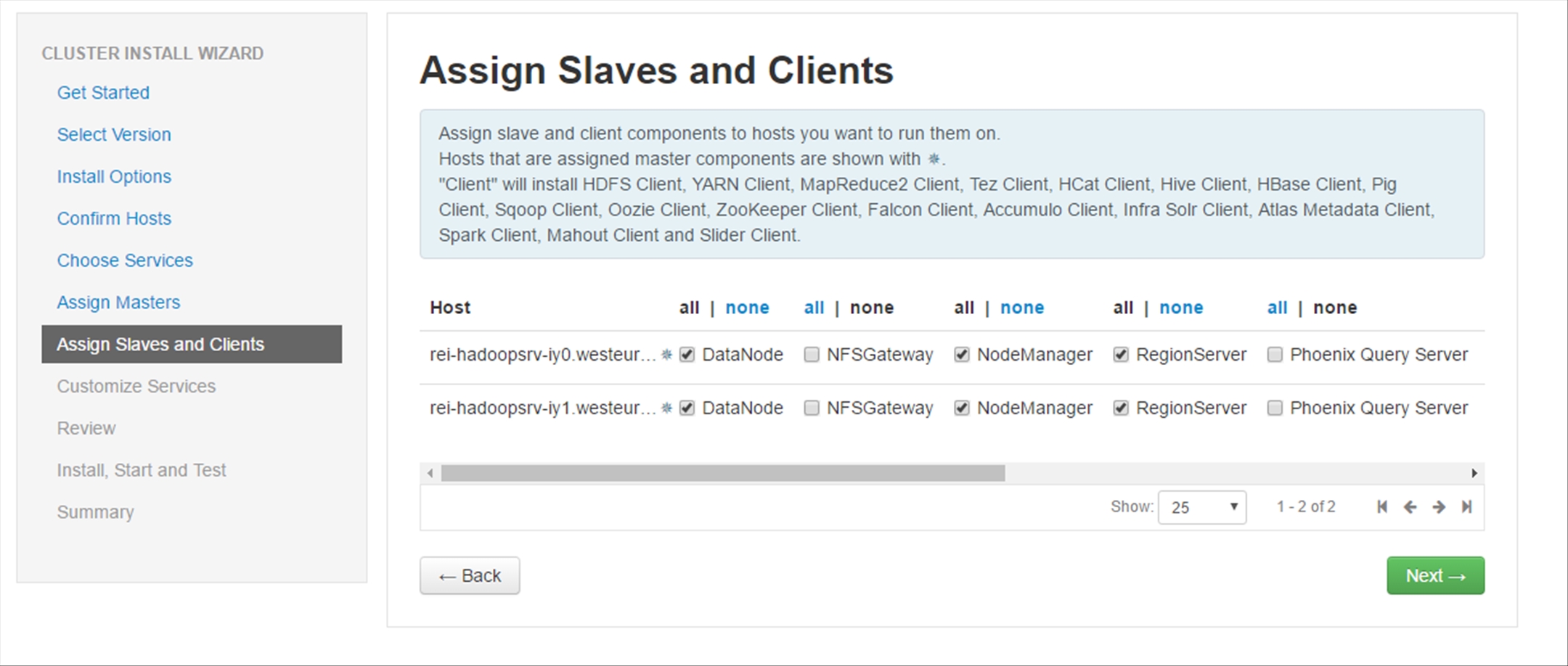
In the Customize Services section, any of the Services that have a red number beside them require your attention. In all of the cases of this walkthrough, each of the matching services requires that you type in a password. Do this for each service as required, scroll down to the bottom of the page and click Next.
Note: After clicking on Next, if you recieve any configuration warnings, choose to proceed anyway.
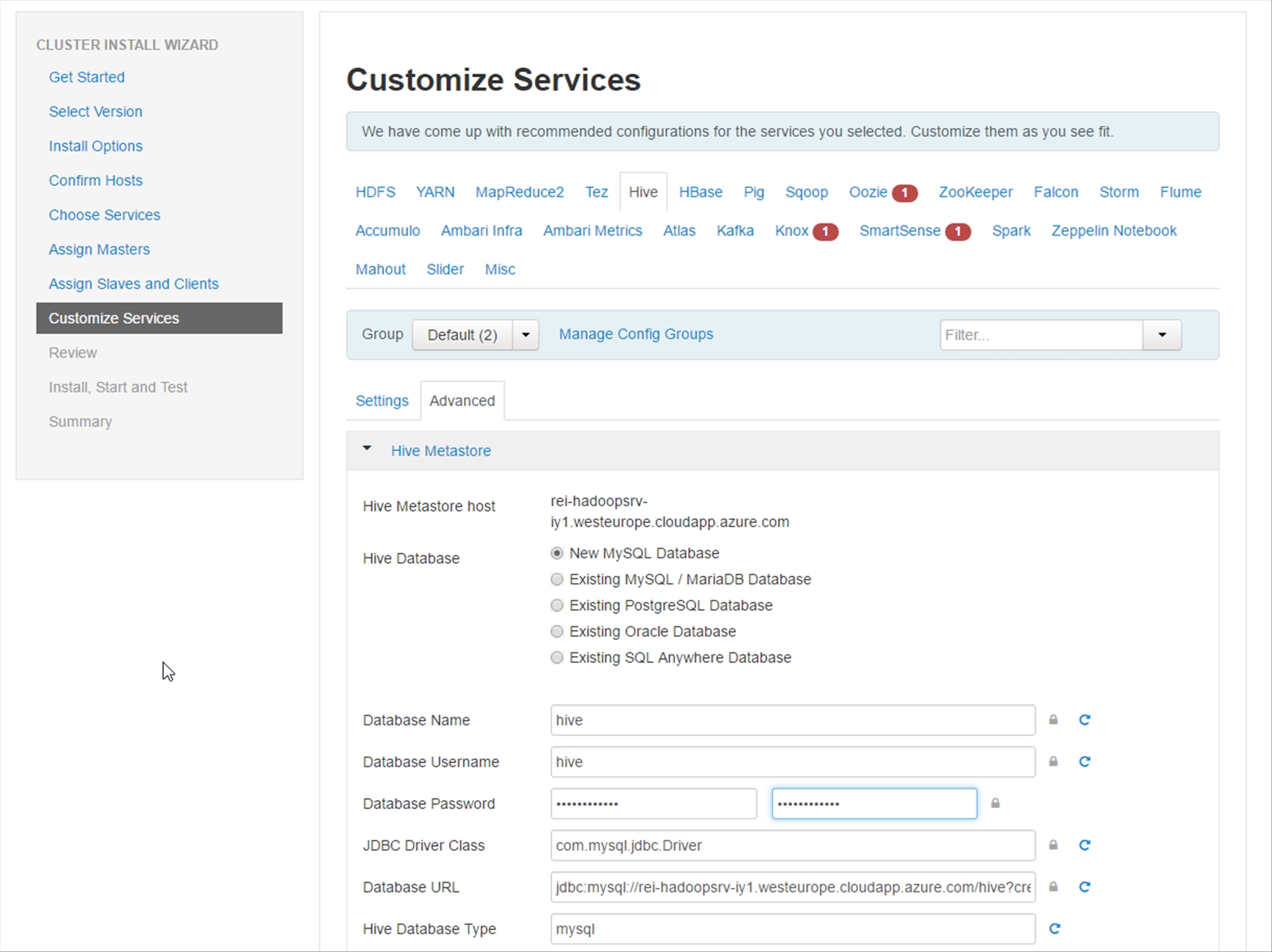
Review the configuration and then click on Deploy.
The selected Services will then be installed and started; on average, the entire process takes 30 minutes.
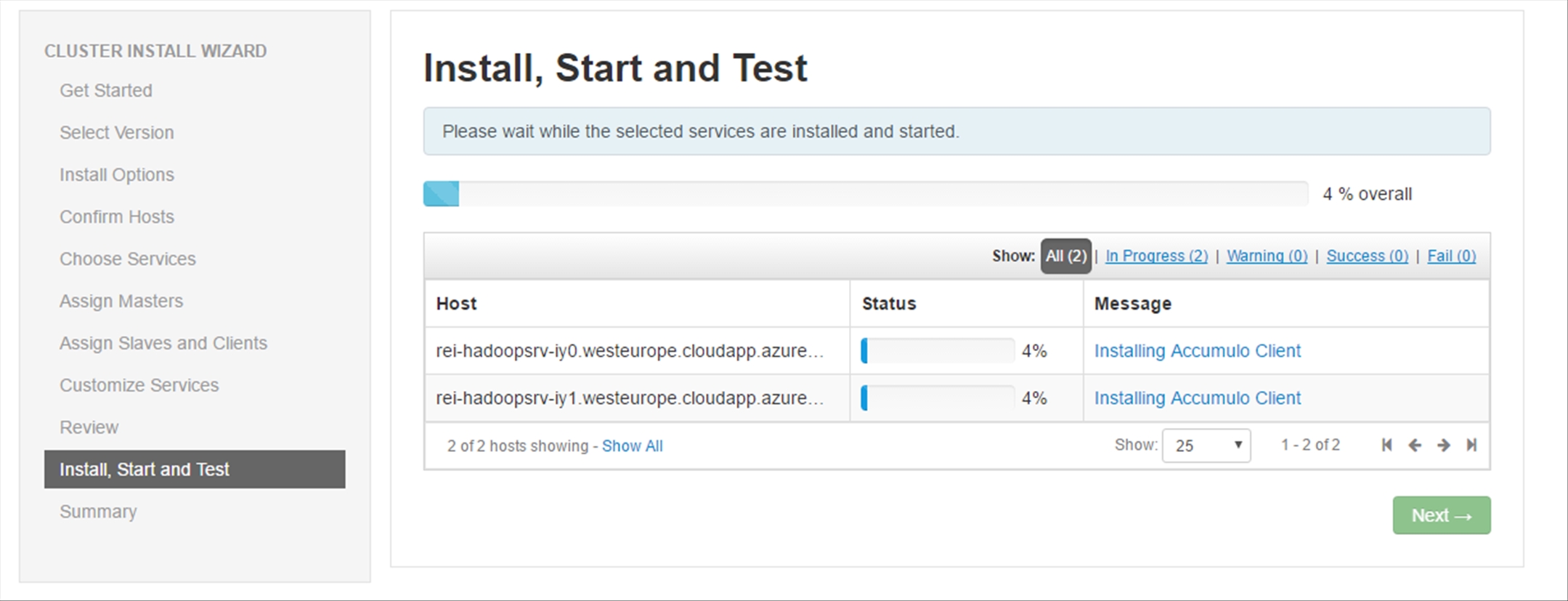
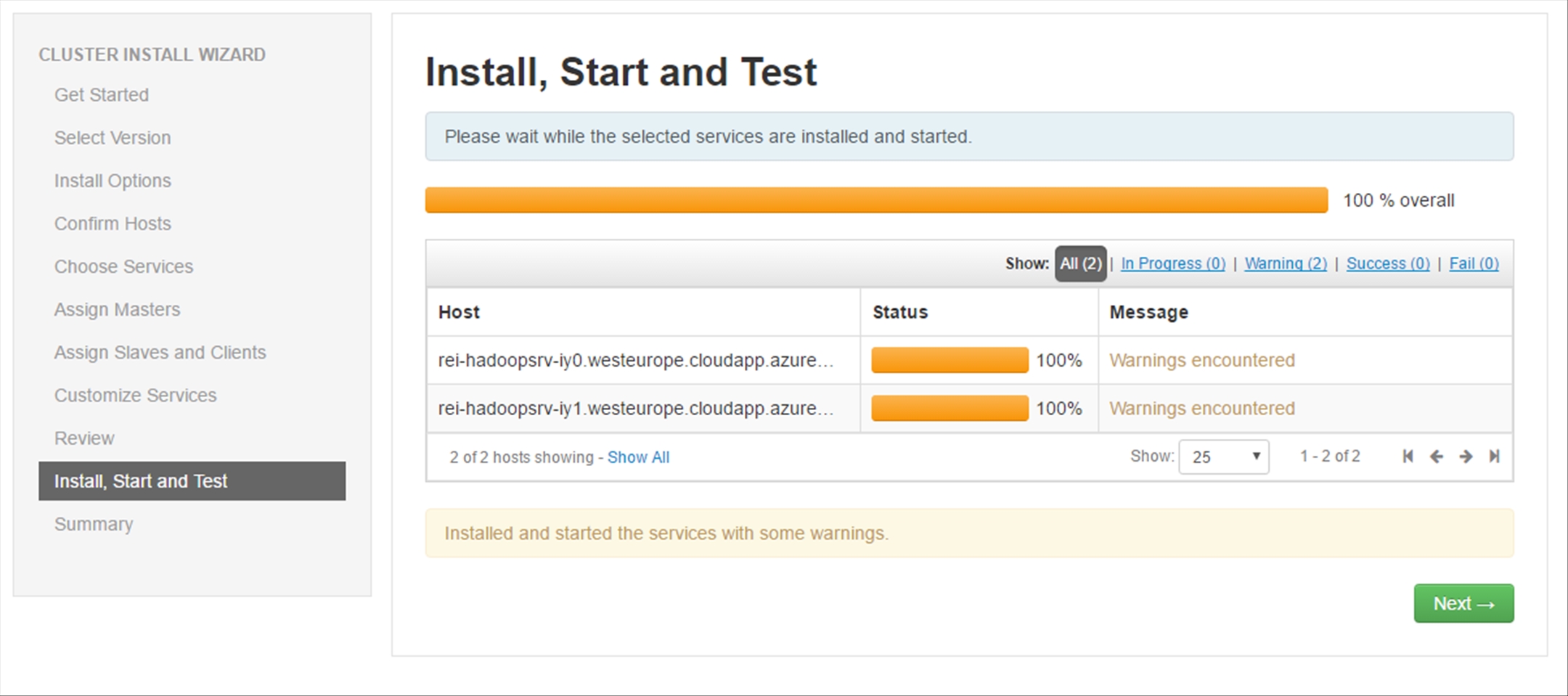
Once the installation is completed, ignore the warnings and click Next.
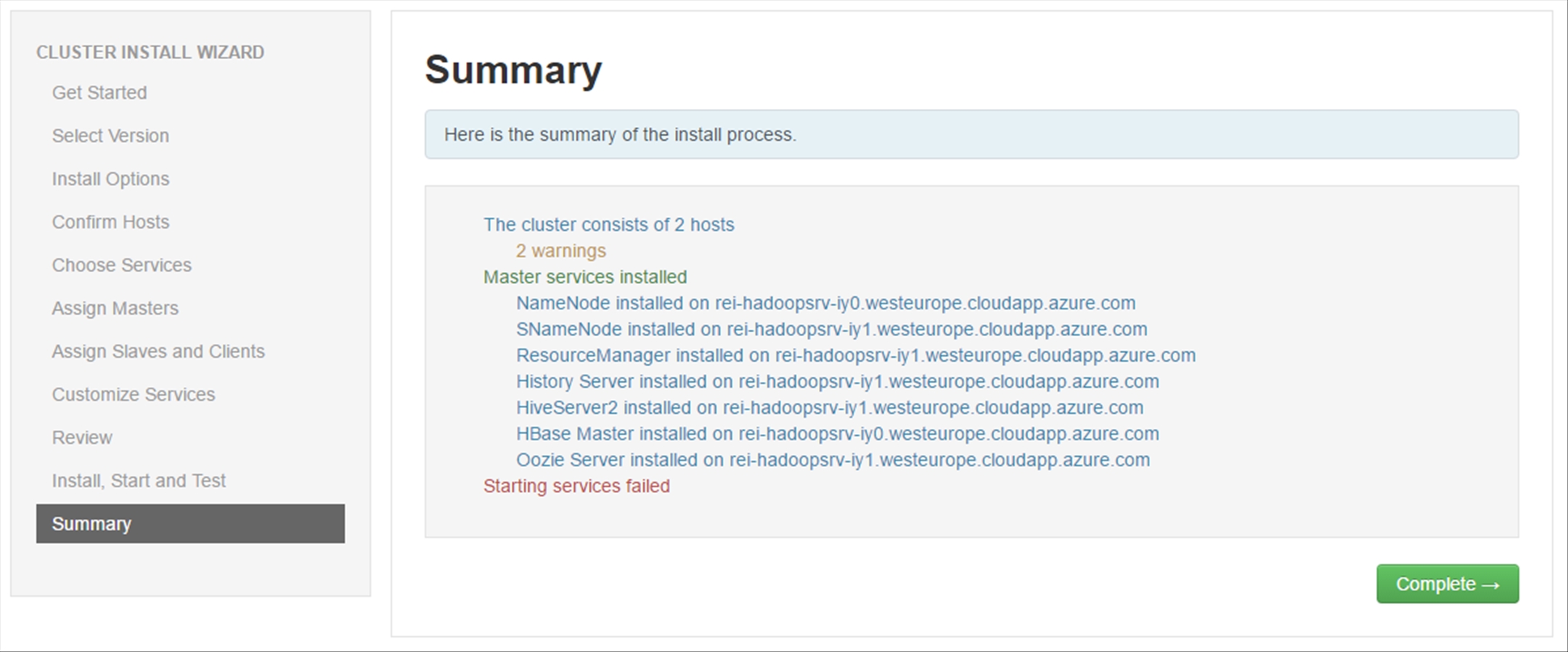
Review the installation Summary and click on Complete.
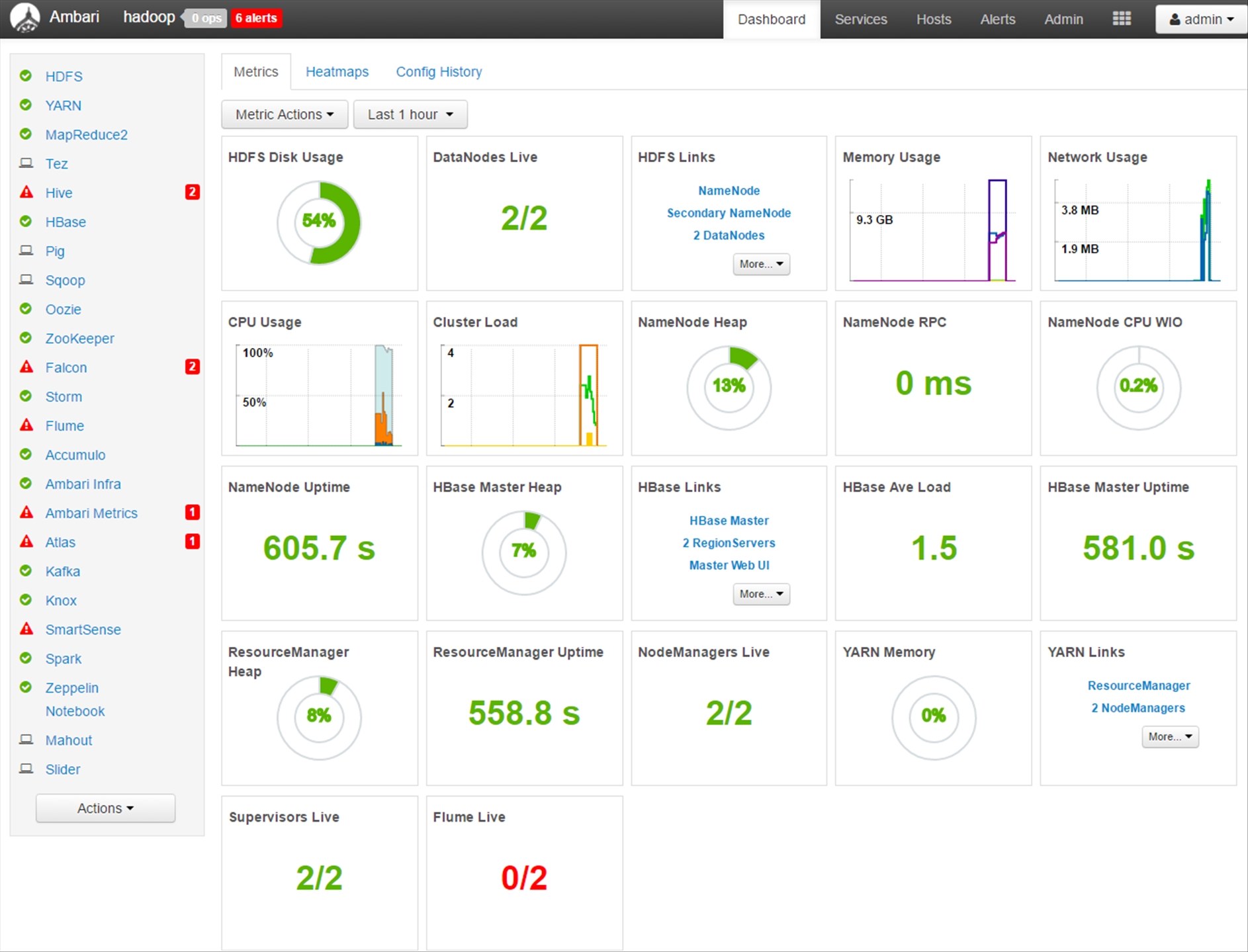
Afterwards, you will be redirected to the Ambari Dashboard.
Closing
This article covers how to deploy a Hadoop Cluster using Apache Ambari running on Linux Virtual Machines in Azure from an ARM Template.

